Other Large Language Models (LLMs)
The future of search engine optimization (SEO) is unfolding in real time, with large language models (LLMs) shifting the focus from traditional keyword-based search to conversational, intent-driven search experiences.
As artificial intelligence (AI) models improve their ability to interpret human language and provide context-aware responses, businesses face both new opportunities and challenges.
On the one hand, AI search allows forward-thinking brands to establish authority in highly specific niches and meet users at the exact point of need. On the other hand, this transition also means tougher competition and raises the bar for visibility.
Bain & Co. reports that approximately 80% of online users now rely on “zero-click” results in at least 40% of their searches, cutting organic traffic by 15% to 25%. How do you raise brand awareness and engage with your target audience when clicks and site visits are disappearing?
Learn about the hype surrounding large language models, their impact on SEO and how you can maintain AI visibility in a zero-click world.
Large language models (LLMs) are a category of deep learning models trained on massive datasets, capable of recognizing and interpreting natural language and other types of complex data.
Unlike traditional software that follows explicit programming instructions, LLMs are built on a transformer architecture. This design allows the model to understand context, meaning and relationships between long passages of text rather than processing words in isolation.
The term “large” in LLM refers to two things:
- Scale of training data: LLMs are trained on vast amounts of data collected from books, websites and other sources.
- Number of parameters: Parameters are the variables used by LLMs to make predictions or decisions. Advanced LLMs use billions (sometimes even trillions) of parameters in their neural networks, which allows them to handle complex tasks and produce outputs that closely resemble human communication.
Some LLMs, such as ChatGPT (Plus, Pro and Enterprise accounts), Perplexity AI, Microsoft Copilot and Google Gemini Advanced, can access the web in real time, enabling them to pull up-to-date information related to the user’s query. However, just like any search engine, the value of their responses depends on the quality and reliability of the sources they draw from.
What Are Multimodal LLMs?
Multimodal large language models are advanced versions of standard LLMs that can process and generate content across multiple types of data, such as text, audio, images and even video.
This cross-modal reasoning capability enables these systems to:
- Generate rich, contextual descriptions of images or videos.
- Answer complex questions about multimedia content.
- Link visual elements to textual descriptions or audio cues.
- Generate content, such as images or voice responses, across modalities.
As the technology matures, multimodal LLMs are expected to transform how businesses connect with consumers online. For marketers and SEO professionals, this means search will no longer be limited to typed queries. Instead, users will increasingly search through voice, images and even video snippets expecting context-rich answers in return.
The challenge now is to adapt digital marketing strategies to this new artificial intelligence search reality.
Are LLMs the Same As AI?
LLMs are not the same as artificial intelligence (AI) itself, and they’re not interchangeable terms. When we talk about LLMs like Claude AI, ChatGPT, Perplexity or other AI search engines, we’re actually referring to a very specific type of technology within a much larger AI ecosystem.
To truly understand large language models, we need to step back and see where they fit in the broader world of artificial intelligence search innovations.
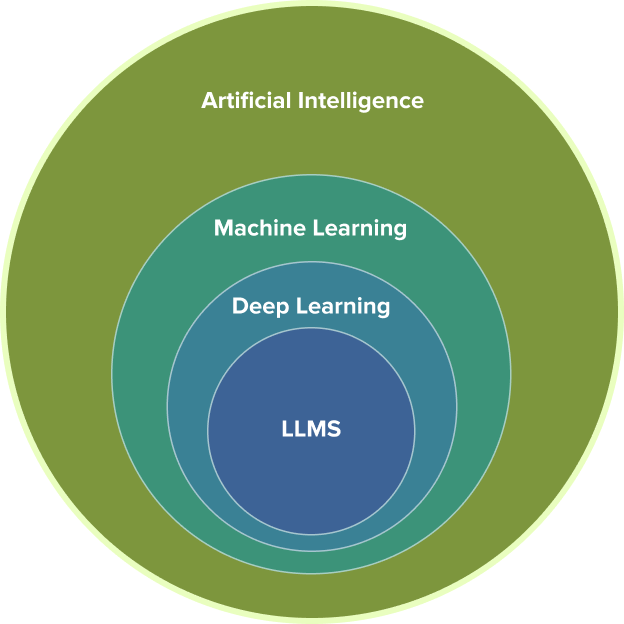
- Intelligent machines
Broadly defined - Pattern Recognition
Learning general patterns from data - Neural Networks
Learning general patterns in unstructured data (i.e. images, text, audio, etc.) - Large Language Models
Learning to understand natural language (i.e. text)
Artificial Intelligence
AI refers to intelligent machines designed to perform tasks that typically require reasoning, problem-solving or decision-making. This could be anything from a simple rule-based system that plays tic-tac-toe to the sophisticated chatbots and alternatives to ChatGPT we interact with today.
Machine Learning (ML)
ML is a subfield of AI focused on teaching machines to recognize patterns in data. Instead of following hard-coded rules, ML models learn from examples. Once a model identifies a pattern, it can apply that understanding to new information. This is the foundation of most modern AI search engines and other applications.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a field within ML that handles unstructured data, such as texts, images and audio. It relies on artificial neural networks or computational systems loosely inspired by how neurons in the human brain process information.
Large Language Models
LLMs are a specialized application of deep learning that focuses exclusively on understanding and generating human language.
LLMs and AI search engines use deep learning to mimic the human brain’s ability to handle complex reasoning and understand how words, characters and sentences function together.
Instead of reading texts sequentially (one word at a time), LLMs can analyze entire sequences of words simultaneously and determine which words are most relevant to each other.
For example, in the sentence, “Tom put the book on the table and opened it.”
The model can identify that “it” refers to “the book,” not “the table.” This ability to track relationships across long passages enables LLMs to generate context-aware responses to user queries.
How Are LLMs Trained?
Training an LLM involves teaching the model to predict the next word in a sequence. This might sound simple, but when repeated across trillions of examples, it allows the model to learn grammar, facts, reasoning patterns and even stylistic nuances.
The process looks like this:
Tokenization
Embedding
Next-Word Prediction
Parameter Optimization
1. Tokenization
Before any text can be processed, it must be broken down into smaller units called tokens (e.g., complete words, parts of words, characters). This tokenization process allows the model to work with a standardized vocabulary.
2. Embedding
Each token is converted into numerical representations called embeddings. Words with similar meanings have embeddings that are close together, creating a kind of “map” of language. This lets the model understand not just individual words, but also their relationships to one another.
3. Next-Word Prediction
Once tokenized and embedded, the model is trained to predict the next token in a sequence. For example, given the text “The cat sat on the,” the model learns that “mat ” is a likely continuation. With enough examples, it begins to capture grammar rules, linguistic styles and factual links.
4. Parameter Optimization
Every wrong prediction leads to small adjustments in the model’s internal parameters. This process, called backpropagation, gradually reduces the errors and improves output accuracy. These refinements make the model more adept at generating coherent, context-aware language.
The broad training approach of LLMs results in systems with surprisingly diverse capabilities. Because they are trained on massive amounts of data, large language models and AI search engines demonstrate remarkable versatility across numerous domains and tasks.
COMMON LLM FEATURES AND CAPABILITIES
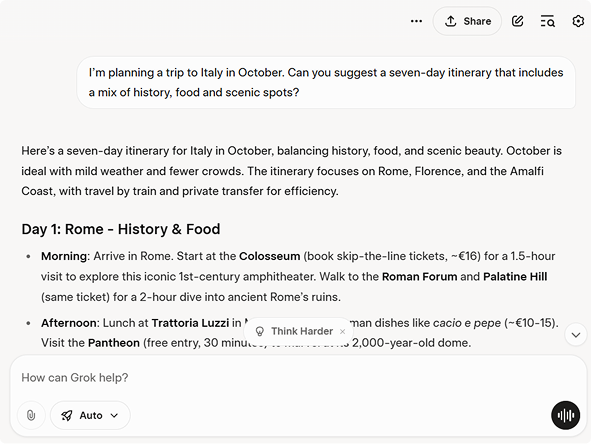
1. Conversational AI Search Experiences
Artificial intelligence search tools, such as Claude AI, Grok and other alternatives to OpenAI’s ChatGPT, are trained to interpret and generate human-like responses across diverse topics.
Unlike traditional search engines that return a list of links, these systems provide direct, context-aware answers and, in some cases, it can retrieve and provide data in real time.
Key Features:
- Natural language understanding and generation
- Context retention across conversation turns
- Multi-turn dialogue management
- Personalized responses based on user history and preferences
An example using Grok:
2. Content Generation
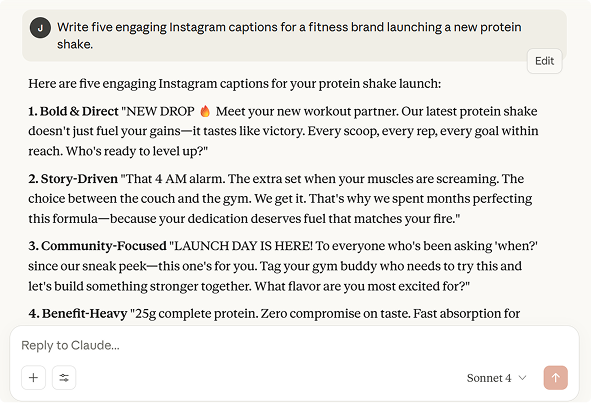
One of the most popular applications of LLMs is content creation. Businesses and individuals are increasingly using LLM search tools like Perplexity AI, Claude, ChatGPT and Copilot to assist with brainstorming ideas, doing research, writing drafts and even editing text.
Key Features:
- Multi-format content creation (i.e., articles, emails, social media posts, scripts, etc.)
- Style and tone adaptation
- SEO-optimized content generation
- Brand voice consistency
- Creative and technical writing capabilities
An example using Claude AI:
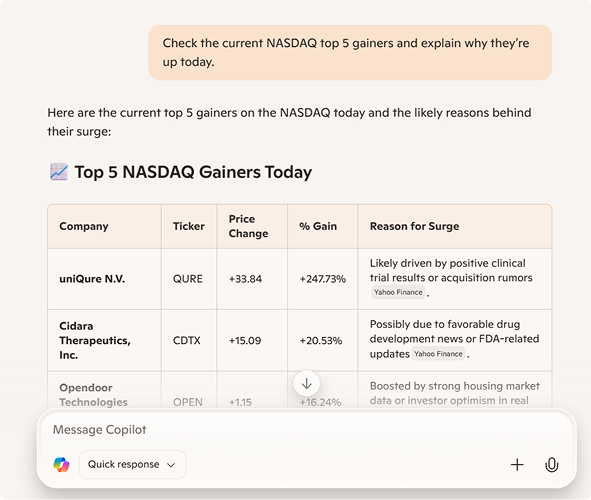
3. Real-Time Information Access
Some LLM search tools integrate with the web or proprietary databases to fetch up-to-date answers. This capability sets them apart from static models trained only on historical datasets.
Key Features:
- Web search integration and real-time data retrieval
- News monitoring and analysis
- Market data interpretation
- Event tracking and updates
- Cross-source information synthesis
An example using Copilot:
4. Language Translation
Large language models help break down language barriers by translating text across dozens of languages. Unlike traditional rule-based translation systems, advanced LLMs rely on deep learning and transformer architectures to understand context. This makes translations more natural and human-like.
Key Features:
- Context-aware translation
- Cultural and idiomatic expression handling
- Multilingual support
- Document and conversation translation
- Localization capabilities for different regions
An example using Meta AI:

5. Code Generation and Programming
LLMs have become useful programming assistants, capable of writing, debugging and explaining code across multiple programming languages.
Key Features:
- Multi-language code generation (i.e., Python, JavaScript, Java, C++, etc.)
- Bug detection and debugging assistance
- Code explanation and documentation
- Algorithm optimization suggestions
- Cross-language code translation
An example using ChatGPT Search:
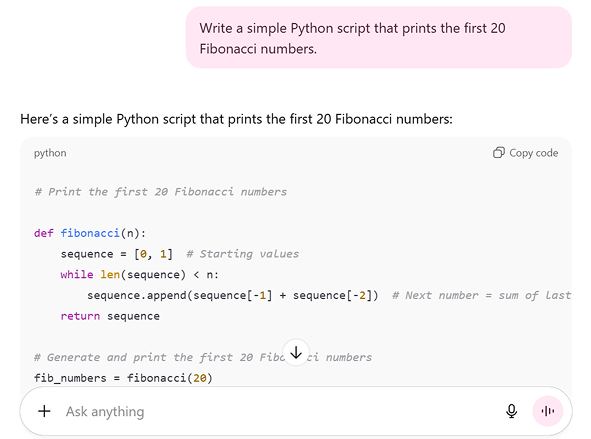
6. Summarization and Analysis
From condensing long research papers to analyzing meeting transcripts, LLM search tools are increasingly used for document review, research synthesis and data extraction. They can quickly scan large volumes of documents and distill the most important insights.
Key Features:
- Document summarization
- Sentiment analysis
- Data pattern recognition
- Comparative analysis across sources
- Key information extraction
An example using Perplexity AI Search:
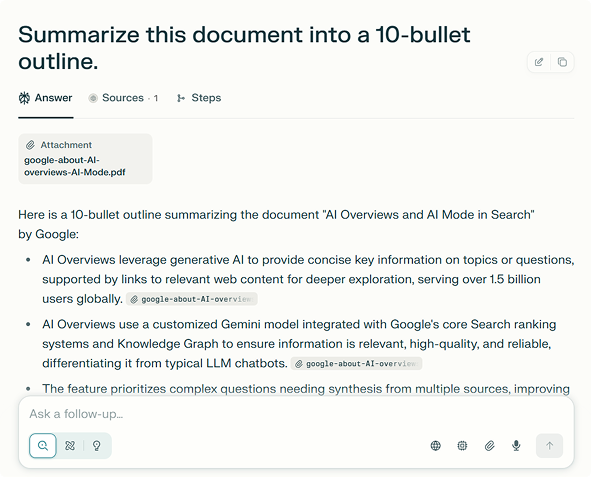
7. Adaptability
One of the most remarkable features of LLMs is their ability to adapt to new tasks, domains and requirements through various training techniques.
Key Features:
- Fine-tuning for specific domains or tasks
- Few-shot learning capabilities
- Prompt engineering for task adaptation
- Multimodal integration (text, images, audio)
- Continuous learning and improvement
What is few-shot learning?
Few-shot learning is a training approach in machine learning where a model is able to perform a new task or understand a new concept after being given only a small number of examples.
Instead of retraining the model, you provide it with a short set of examples (called shots) directly in the prompt. The model uses those examples to infer the desired pattern or style and then applies it to new inputs.
What Are the Limitations of LLMs?
Despite these LLM and AI search engine capabilities, they also come with several limitations that affect their reliability and ethical use.
LLM LIMITATIONS
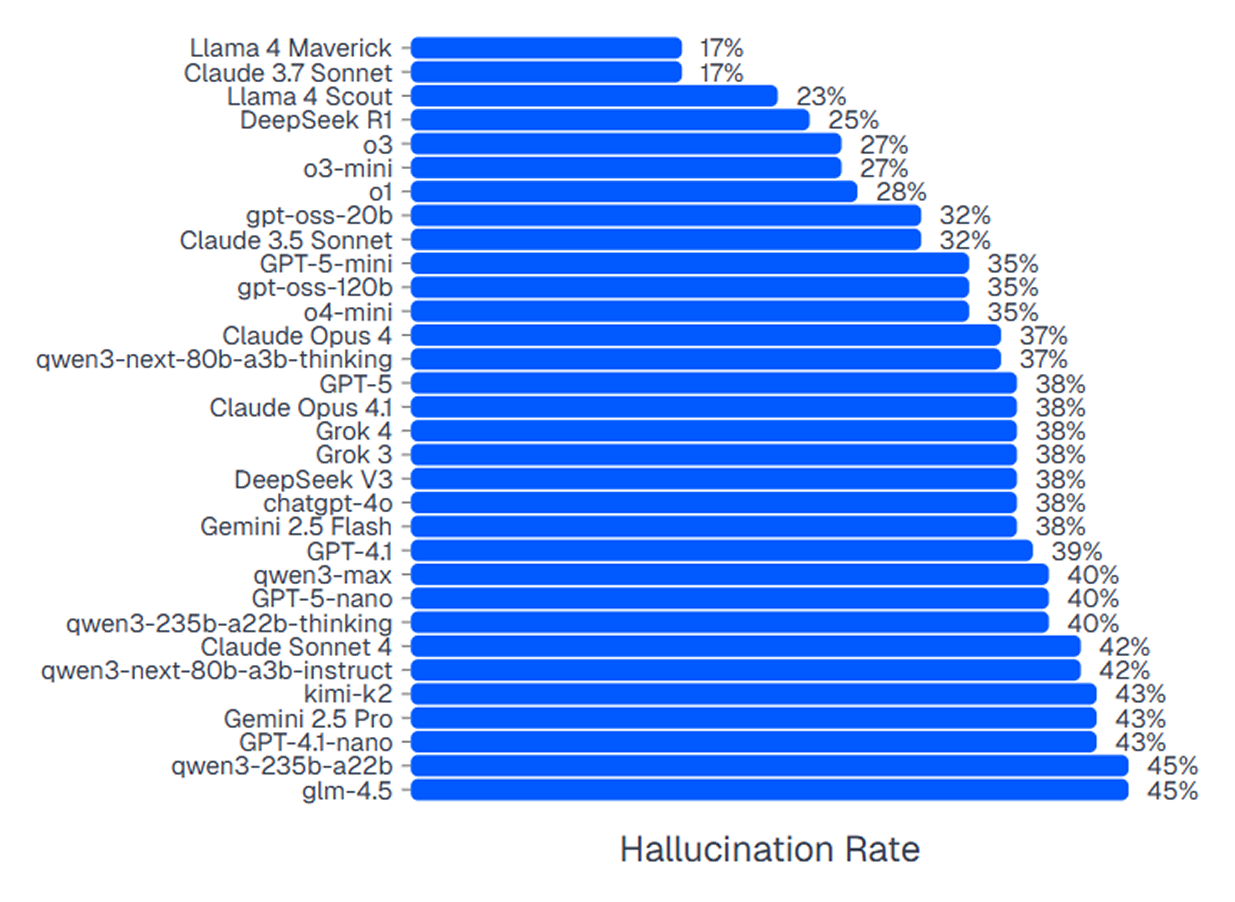
1. Hallucinations
Hallucinations occur when AI search engine models confidently present false facts, fabricated citations or non-existent events as if they were true.
Research shows significant variation in hallucination rates across different models. As indicated in the graph below, Claude 3.7 Sonnet appears to have the lowest hallucination rate of 17%:
This limitation poses major risks in research and decision-making contexts where accuracy is critical.
2. Bias and Fairness
Large language models inherit and amplify social biases present in their training data, resulting in outputs that may contain biased, offensive or unbalanced representations of groups and cultures.
Companies like Anthropic (Claude’s developer) are experimenting with constitutional AI to make models align better with ethical principles, but total bias removal is nearly impossible.
3. Context and Memory Limits
LLMs operate within a context window, meaning they can only process and remember a limited amount of information. This restriction leads to challenges in long conversations, document analysis or projects requiring deep continuity. Once the token limit is exceeded, the model may forget earlier parts of the dialogue, reducing consistency and reliability.
4. Data Privacy Concerns
Large language models are trained on vast amounts of publicly available data, which may include personal or sensitive information. This raises several risks:
- Potential leakage of private data in responses
- Use of data without explicit consent
- Concerns about how user interactions are stored or reused
For enterprises in regulated industries like healthcare, finance or government, these privacy concerns limit adoption unless models are deployed with strict safeguards.
5. Real-Time Knowledge Gaps
Even the most advanced LLM search engine systems are limited by the data they were trained on. If a model was last updated in 2023, it will lack awareness of events, research or policies from 2024 onward unless connected to retrieval systems.
Some LLMs like Perplexity AI Search and alternatives to ChatGPT attempt to solve this with real-time web integration and citations. However, LLMs without retrieval augmentation often provide outdated or incomplete answers.
6. Ethical and Legal Challenges
The rapid rise of LLMs has created a complex set of ethical and legal issues, including:
- Copyright: Models may generate outputs that resemble or reproduce copyrighted material without attribution.
- Misinformation: Their ability to generate convincing but false content raises concerns about manipulation and fake news.
- Accountability: When an LLM produces harmful or incorrect content, it’s unclear who is legally responsible — the developer, the deployer or the end user.
- Regulation: Governments are increasingly exploring AI-specific legislation to address safety, transparency and liability.
These challenges underscore the importance of human oversight and evolving governance frameworks.
While there are dozens of major large language models and hundreds more that are arguably significant, these dominate in terms of adoption:
| Model | Developer | Core Strength | Multimodal Support | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI |
Perplexity AI, Inc. | Real-time search | Limited (mainly text + some image inputs) | Free tier + Pro subscription |
 Claude AI Claude AI |
Anthropic | Safety and reasoning | Text, images | Free tier + Paid (Claude Pro, enterprise licensing) |
 Copilot Copilot |
Microsoft | Microsoft integration | Text, images, voice | Included in Microsoft 365 subscriptions + Enterprise tiers |
 Mistral AI Mistral AI |
Mistral (Paris) | Efficiency and speed | Limited (mostly text) | Open-source/free models + Enterprise partnerships |
 Meta AI Meta AI |
Meta (Facebook) | Open-source flexibility | Text, images, video | Free (open-source releases) + integrated into Meta products |
 Grok Grok |
xAI (Elon Musk) | Real-time social data | Text, images | Free + Paid subscription |
1. Perplexity AI Search
Perplexity Search functions as an “answer engine” that blends the conversational experience of chatbots with the precision of real-time search. Unlike traditional search engines that return a list of links, Perplexity Search delivers direct (mostly linked to the original sources) answers pulled from live web sources.
Best For: Individuals looking for OpenAI alternatives and prioritizing accuracy and trustworthiness in AI-powered search
STRENGTHS
- Real-time web search integration
- Source citations
- Clean, ad-free interface
- Mobile and web applications
- Maintain context in multi-turn conversations
LIMITATION
- Less creative writing capabilities compared to other ChatGPT alternatives
- Limited customization options for specific use cases
- Heavy reliance on internet connectivity
2. Claude AI
Claude AI stands out among ChatGPT alternatives with its strong focus on AI safety, ethics and reliability. The latest Claude 4 Sonnet features an impressive 200K-token context window and introduces “extended thinking mode” for enhanced reasoning capabilities.
Best For: In-depth document analysis, creative writing or extended conversations
STRENGTHS
- Extreme context window
- Constitutional AI approach for safe outputs
- Superior reasoning abilities
- Strong coding and analytics capabilities
- Multimodal processing (text and images)
LIMITATION
- Usage restrictions
- Can be conservative in responses due to safety measures
- Higher cost compared to some OpenAI alternatives
- Limited availability in certain regions
3. Copilot
Microsoft Copilot integrates GPT-4 technology across the Microsoft ecosystem, providing AI assistance directly within Office applications, Windows and Bing Search. This integration makes it one of the most accessible OpenAI alternatives for business users.
Best For: Business productivity and document creation
STRENGTHS
- Microsoft Office suite integration
- GPT-4 powered responses
- Multimodal capabilities (text, images, voice)
- Real-time web search through Bing
- Enterprise-grade security and compliance
LIMITATION
- Heavily tied to the Microsoft ecosystem
- Subscription costs can be significant for businesses
- Performance depends on the underlying GPT models
- Limited customization outside Microsoft products
4. Mistral AI
Paris-based Mistral AI has quickly gained attention as a European alternative to U.S.-dominated models. Its latest Mitral Small 3.1 is designed for low-latency applications while maintaining competitive accuracy.
Best For: Small to medium business implementations
STRENGTHS
- Open-source availability
- Excellent performance-to-size ration
- Low latency responses (150 tokens per second)
- European data privacy compliance
- Cost-effective for businesses
- Can run on limited hardware resources
LIMITATION
- Smaller community compared to larger ChatGPT alternatives
- Less extensive training data than some competitors
- Limited multimodal capabilities
- Fewer third-party integrations
5. Meta AI
Meta (formerly Facebook) has a dual strategy: consumer AI experiences inside Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp and Messenger and open-source LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) models for the research community.
Best For: General users of Meta apps and researchers looking for open-source LLMs
STRENGTHS
- Multimodal processing (text, images, video)
- Large context windows (up to 256K tokens)
- Strong multilingual support
- No usage fees for most applications
- Excellent performance across various tasks
- Regular model updates and improvements
LIMITATION
- Limited consumer assistance
- Privacy concerns due to Meta’s data history
- Open-source LLaMA requires careful handling to prevent misuse
6. Grok
Created by Elon Musk’s company xAI, Grok is integrated directly into X (formerly Twitter). It is marketed as a “truth-seeking AI” that aims to be more transparent, less censored and more humorous than its competitors. Like other alternatives to ChatGPT, Grok 3 introduces advanced reasoning capabilities and real-time information access.
Best For: X users who want a built-in conversational assistant
STRENGTHS
- Real-time social media and news access
- Unique personality and conversational style
- Strong reasoning capabilities
- Integration with the X platform for current events
- Advanced search and analysis features
LIMITATION
- Newer model with a less proven track record
- Primarily focused on the X ecosystem
- Higher costs for premium features
- Less extensive documentation and support
Artificial intelligence SEO builds on traditional optimization approaches but focuses more on content authority, clarity and contextual relevance. The goal is to rank in traditional search engines AND be cited in AI-generated responses.
Follow these artificial intelligence search engine optimization tips and ensure your brand shows up where people increasingly go for answers:
LLM OPTIMIZATION TIPS
1. Optimize for E-E-A-T Principles
Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) remain at the core of both traditional and LLM SEO. Large language models heavily prioritize content that demonstrates these qualities, as they’re trained to surface the most reliable and authoritative information.
Some LLM or NLP SEO tips:
- Publish content written or reviewed by subject matter experts.
- Display author bios and professional credentials to establish authority.
- Use original data, case studies and customer testimonials to demonstrate trustworthiness.
- Regularly update content to ensure freshness and reliability.
2. Use Structured Data and Schema
Schema markup is critical for artificial intelligence optimization because it helps LLMs understand your content’s context, purpose and relevance to user queries. Adding schema markup and semantic organization significantly improves your chances of being cited in AI responses.
Follow these artificial intelligence search engine optimization tips:
- Add frequently asked questions (FAQs) schema to pages covering common customer questions.
- Use product and review schema for eCommerce content.
- Format key takeaways in bullet points and tables for clarity.
- Ensure metadata is accurate and descriptive for improved parsing.
3. Optimize for Conversational Search Patterns
Unlike traditional keyword searches, people interact with LLMs and AI search engines in natural language. Large language model optimization requires anticipating how users phrase full questions and scenarios rather than single keywords.
Some NLP SEO best practices:
- Incorporate long-tail, conversational questions into your content.
- Create Q&A sections that mirror how users would ask LLMs.
- Write in a clear, conversational tone instead of keyword-stuffed language.
- Include examples, use cases and step-by-step explanations that match AI-driven user intent.
4. Build Your Brand Authority
LLMs pull data from trusted and widely recognized sources. Building a strong brand presence boosts your chances of being cited by an LLM search engine.
Build authority with these artificial intelligence SEO tips:
- Earn authoritative backlinks from respected industry sites.
- Establish thought leadership with guest articles, podcasts and webinars.
- Maintain consistent brand messaging across the web.
- Encourage user-generated content (testimonials, reviews) that reinforces brand credibility.
5. Monitor AI Search Performance
LLM-driven search is dynamic and your visibility within AI-generated responses may shift over time. Ongoing monitoring and testing are key to long-term success in artificial intelligence search engine optimization.
Follow these LLM SEO tips:
- Test prompts across Claude, Perplexity Search, Copilot and other LLMs to see if your brand is cited.
- Track changes in how AI search engines summarize your content versus competitors.
- Adjust content formats (FAQs, listicles, guides) to increase visibility.
- Use analytics and brand monitoring tools to measure AI visibility.
Embrace the AI-Powered Future
The shift toward artificial intelligence search represents the most significant change in information discovery since the advent of search engines themselves. Businesses that recognize this transformation and adapt their LLM SEO strategies accordingly will find unprecedented opportunities for visibility and growth in the AI-dominated future.
At Thrive Internet Marketing Agency, we’ve seen firsthand how LLM optimization impacts visibility. By applying and testing these artificial intelligence SEO strategies across emerging platforms, we achieved an +101% increase in traffic from Perplexity Search and a +3,017% increase in traffic from Claude AI. These results underscore how quickly brands can gain traction when content is optimized for AI visibility.
Do not resist change. Begin your artificial intelligence optimization with Thrive and take control of how LLMs represent your brand.
Frequently Asked Questions About Large Language Models
CAN YOU INFLUENCE AI SEARCH ENGINE RESULTS?
Yes. You can influence AI search engine results through proper LLM optimization strategies, including creating authoritative content, using structured data, building brand authority and optimizing for conversational search patterns.
WHAT ARE ALTERNATIVES TO OPENAI’s CHATGPT?
The most popular OpenAI alternatives, aside from those already highlighted (Perplexity AI Search, Claude, Copilot, Mistral AI, Meta AI and Grok), include Google Gemini, Character.AI and Inflection AI.
WHAT ARE MULTIMODAL LLMs?
Multimodal LLMs are advanced versions that can process and generate content across multiple data types, including text, audio, images and video.
ARE LLMS THE SAME AS AI?
No. AI is a broad field covering many technologies, while LLMs are a specific type of deep learning model focused on natural language processing and generation.
WHAT ARE LLM HALLUCINATIONS?
Hallucinations occur when LLMs confidently present false facts, fabricated citations or non-existent events as true.
HOW DOES NLP SEO AFFECT CONTENT FORMATTING?
NLP SEO emphasizes clear content formatting with descriptive headers, bullet points, numbered lists, FAQ sections and tables that LLMs can easily parse and extract relevant information from for user queries.
HOW DOES LLM SEARCH ENGINE OPTIMIZATION DIFFER FROM TRADITIONAL SEO?
Traditional SEO targets keyword rankings in search engines, while artificial intelligence optimization adapts content for natural language models, ensuring clarity, authority and contextual relevance to increase chances of being referenced in AI-generated results.
HOW CAN BUSINESSES PREPARE FOR THE SHIFT TO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE OPTIMIZATION?
Businesses should audit existing content for AI readiness, build topical authority through expert content and establish consistent brand mentions across authoritative sources to prepare for artificial intelligence optimization.